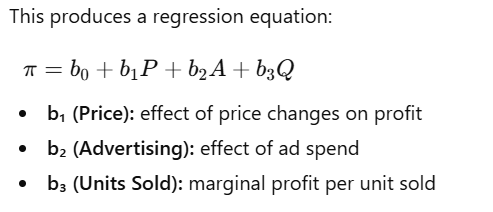|
PythonPlaza -
Python & AI
|
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms
Linear/Multiple Linear Regression
Linear regression is a kind of supervised machine learning that uses data where each data point has a known labelled data (output data). Linear Regression typically has 1 independent variable that affects the dependent variable. It tries to find the best straight line that fits the data points. This line shows the relationship between input and output values in a straight way. It helps understand how changes in the input values affect the output values consistently. Once this line is found, it can be used to make predictions for new input values.
The multiple linear regression has several independent variables. Multiple regression is represented as Plane/hyperplane (3D or higher)
Minimizing the Error: Least Squares Method
To find the best-fit line, we use a method called Least Squares. The goal of this method is to make the total of the squared differences between the real data points and the values predicted by the line as small as possible. These differences are known as residuals. The Least Squares estimates the regression coefficients so that the model’s predictions are as close as possible to the actual observed values.
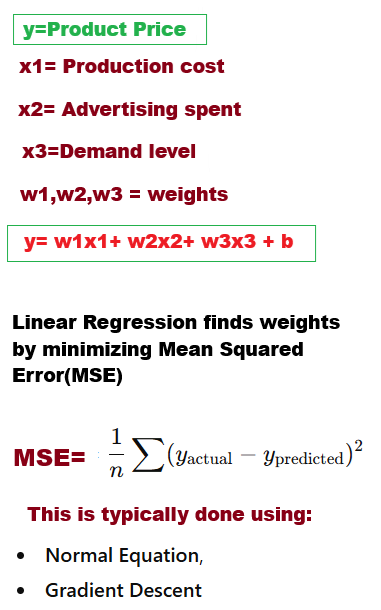
USE CASE 1: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn, predict the product price. The Production cost, Advertising spend, and Demand level are the independent variables.
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
data = pd.read_excel("product_data.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Production_Cost', 'Advertising_Spend', 'Demand_Level']]
y = data['Product_Price']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# -----------------------------------
# 5. Model parameters
# -----------------------------------
print("\nIntercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients:")
for feature, coef in zip(X.columns, model.coef_):
print(f" {feature}: {coef}")
# -----------------------------------
# 6. Evaluate the model
# -----------------------------------
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("\nModel Evaluation:")
print("R² Score:", r2)
print("Mean Absolute Error:", mae)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)
# -----------------------------------
# 7. Predict price for a new product
# -----------------------------------
new_product = pd.DataFrame({
'Production_Cost': [68],
'Advertising_Spend': [13],
'Demand_Level': [37]
})
predicted_price = model.predict(new_product)
print("\nPredicted Product Price:", predicted_price[0])
USE CASE 2: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn to predict the Student Grade. The 'Hours_Studied, 'Attendance_%', 'Previous_Score' are the independent variables.

import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
# https://pythonPlaza.com/linear_school_grade_data.html
data = pd.read_excel("student_data.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Hours_Studied', 'Attendance_%', 'Previous_Score']]
y = data['Final_Grade']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# -----------------------------
# Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# -----------------------------
# Evaluation
print("Predicted grades:", y_pred)
print("Actual grades: ", y_test)
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
Example: Predict a new student’s grade
# New student: [hours_studied, attendance %, previous_score]
new_student = np.array([[6, 85, 78]])
predicted_grade = model.predict(new_student)
print("Predicted final grade:", predicted_grade[0])
USE CASE 3: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn to predict the Profit Optimization. The Price (P), Advertising (A), Units Sold (Q) are the independent variables, and Profit is the dependent variable.
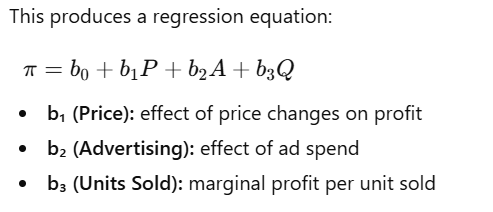
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
Get the Profit Optimization data in Excel
data = pd.read_excel("profit_optimization.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target Price (P)
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Price', 'Advertising', 'Units_Sold']]
y = data['Profit']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Predict profit
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted profit:", y_pred)
print("Actual profit: ", y_test)
#Evaluate the model
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Profit equation (key for optimization)
print("Intercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients [Price, Advertising, Units Sold]:", model.coef_)
#Predict profit for a new business strategy
# Example: Price = 15, Advertising = 165, Units Sold = 460
new_strategy = np.array([[15, 165, 460]])
predicted_profit = model.predict(new_strategy)
print("Predicted profit:", predicted_profit[0])
USE CASE 4: Using Linear Regression with scikit-learn to predict the Patient Response. The Dosage (mg), Age (yrs), Weight (lbs) are the independent variables, and Patient Response is the dependent variable.

import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
Get the Patient Response Data in Excel
data = pd.read_excel("patient_dosage_response.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target Price (P)
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Dosage', 'Age', 'Weight']]
y = data['Patient_Response']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Predict profit
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted responses:", y_pred)
print("Actual responses: ", y_test)
#Evaluate the model
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Profit equation (key for optimization)
print("Intercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients [Dosage, Age, Weight]:", model.coef_)
Predict response for a new patient
# New patient: Dosage=72mg, Age=36yrs, Weight=172lbs
new_patient = np.array([[72, 36, 172]])
predicted_response = model.predict(new_patient)
print("Predicted patient response:", predicted_response[0])