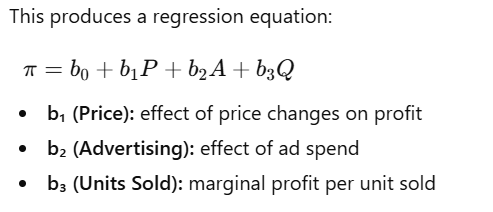|
PythonPlaza -
Python & AI
|
Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms
K-Nearest Neighbors
Although it can be applied to regression tasks, K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) is a supervised machine learning technique that is mostly employed for classification. It produces predictions based on the average value (for regression) or the majority class (for classification) after locating the "k" nearest data points (neighbors) to a given input. KNN is an instance-based and non-parametric learning technique since it does not assume anything about the distribution of the underlying data.
K-Nearest Neighbors is also known as a lazy learner algorithm because, rather than learning from the training set right away, it retains the dataset and acts upon it during classification.
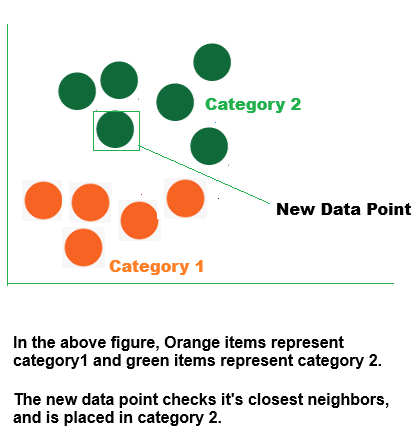
What does "K" stand for in "K Nearest Neighbor"?
The number k in the k-Nearest Neighbors method simply indicates how many neighboring points or points the algorithm should consider while making a conclusion.
For instance, let us say you are determining the type of fruit based on its size and shape. You make comparisons to familiar fruits.
•The algorithm examines the three fruits that are closest to the new one if k = 3.
•The algorithm determines that the new fruit is a mango because the majority of its neighbors are mangos if two of those three fruits are mangos and one is a banana.
Euclidean Distance
Euclidean distance is the most common distance metric used in KNN. For two points, (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), the Euclidean distance is:
√((x2 - x1)² + (y2 - y1)²).
USE CASE 1: Using K-Nearest Neighbors with scikit-learn, predict the product price. The Production cost, Advertising spend, and Demand level are the independent variables.
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
data = pd.read_excel("product_data.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Production_Cost', 'Advertising_Spend', 'Demand_Level']]
y = data['Product_Price']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# -----------------------------------
# 5. Model parameters
# -----------------------------------
print("\nIntercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients:")
for feature, coef in zip(X.columns, model.coef_):
print(f" {feature}: {coef}")
# -----------------------------------
# 6. Evaluate the model
# -----------------------------------
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, y_pred)
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
print("\nModel Evaluation:")
print("R² Score:", r2)
print("Mean Absolute Error:", mae)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)
# -----------------------------------
# 7. Predict price for a new product
# -----------------------------------
new_product = pd.DataFrame({
'Production_Cost': [68],
'Advertising_Spend': [13],
'Demand_Level': [37]
})
predicted_price = model.predict(new_product)
print("\nPredicted Product Price:", predicted_price[0])
USE CASE 2: Using K-Nearest Neighbors with scikit-learn to predict the Student Grade. The 'Hours_Studied, 'Attendance_%', 'Previous_Score' are the independent variables.

import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
# https://pythonPlaza.com/linear_school_grade_data.html
data = pd.read_excel("student_data.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Hours_Studied', 'Attendance_%', 'Previous_Score']]
y = data['Final_Grade']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# -----------------------------
# Predictions
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
# -----------------------------
# Evaluation
print("Predicted grades:", y_pred)
print("Actual grades: ", y_test)
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
Example: Predict a new student’s grade
# New student: [hours_studied, attendance %, previous_score]
new_student = np.array([[6, 85, 78]])
predicted_grade = model.predict(new_student)
print("Predicted final grade:", predicted_grade[0])
USE CASE 3: Using K-Nearest Neighbors with scikit-learn to predict the Profit Optimization. The Price (P), Advertising (A), Units Sold (Q) are the independent variables, and Profit is the dependent variable.
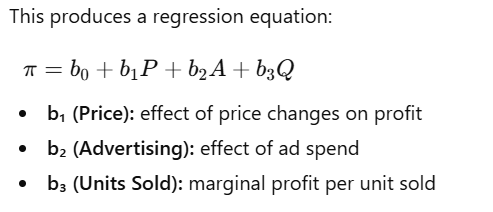
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
Get the Profit Optimization data in Excel
data = pd.read_excel("profit_optimization.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target Price (P)
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Price', 'Advertising', 'Units_Sold']]
y = data['Profit']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Predict profit
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted profit:", y_pred)
print("Actual profit: ", y_test)
#Evaluate the model
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Profit equation (key for optimization)
print("Intercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients [Price, Advertising, Units Sold]:", model.coef_)
#Predict profit for a new business strategy
# Example: Price = 15, Advertising = 165, Units Sold = 460
new_strategy = np.array([[15, 165, 460]])
predicted_profit = model.predict(new_strategy)
print("Predicted profit:", predicted_profit[0])
USE CASE 4: Using K-Nearest Neighbors with scikit-learn to predict the Patient Response. The Dosage (mg), Age (yrs), Weight (lbs) are the independent variables, and Patient Response is the dependent variable.

import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
# -----------------------------------
# 1. Load data from Excel
# -----------------------------------
#sample data can be exported to
#excel from the URL
Get the Patient Response Data in Excel
data = pd.read_excel("patient_dosage_response.xlsx")
print("Dataset Preview:")
print(data.head())
# -----------------------------------
# 2. Define features and target Price (P)
# -----------------------------------
X = data[['Dosage', 'Age', 'Weight']]
y = data['Patient_Response']
# -----------------------------------
# 3. Split into training and testing
# -----------------------------------
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=42
)
# -----------------------------------
# 4. Train the Linear Regression model
# -----------------------------------
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
#Predict profit
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print("Predicted responses:", y_pred)
print("Actual responses: ", y_test)
#Evaluate the model
print("\nMean Squared Error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
print("R² Score:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
#Profit equation (key for optimization)
print("Intercept:", model.intercept_)
print("Coefficients [Dosage, Age, Weight]:", model.coef_)
Predict response for a new patient
# New patient: Dosage=72mg, Age=36yrs, Weight=172lbs
new_patient = np.array([[72, 36, 172]])
predicted_response = model.predict(new_patient)
print("Predicted patient response:", predicted_response[0])